


|
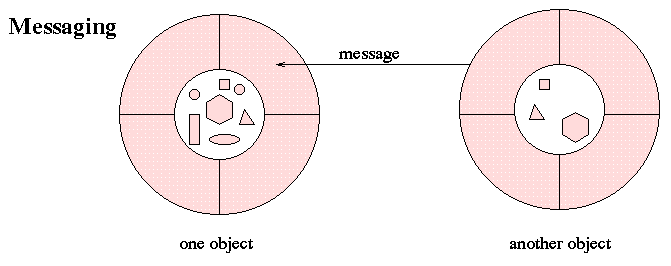
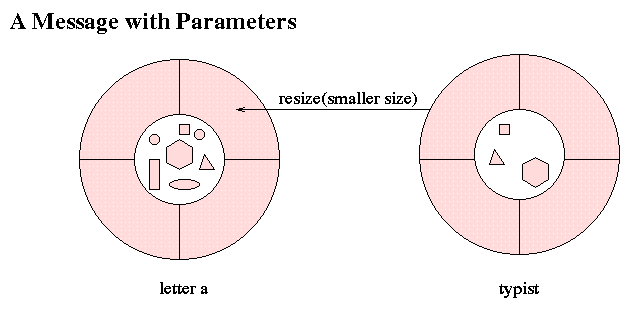
software systems consist of objects that have state and behavior and that communicate by messages.What does this mean?
As the name object-oriented suggests, objects are most important in this style of programming. This contrasts with procedural languages that focus on executing procedures in the computer. Here, you may think of real-world objects such as people, cars, houses, and so on. Common characteristics of these real-world objects are that they all have a state and a behavior. For example, people have state (name, length, weight, etc.) and behavior (talk, walk, sit, ...). Cars have state (speed, direction, fuel consumption, ...) and behavior (start, accelerate, brake, stop, turn, ...).
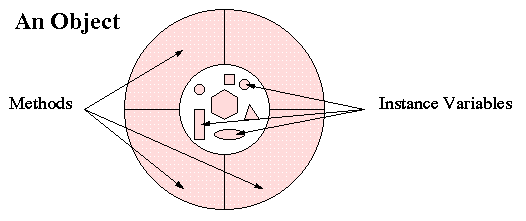
In an object-oriented language, objects are modeled in the same way: they have state expressed in instance variables and behavior implemented with methods. The methods manipulate the variables that define state. For example, documents on a Website have state (title, URL, content-type) and behavior (open, close, reload, ... ). Screen characters have state (name, font, size, position, ... ) and behavior (draw, resize, italicize, ...). In short,
In an object-oriented language, objects consist of data (instance variables) and operations (methods) to manipulate the data.In graphical terms: