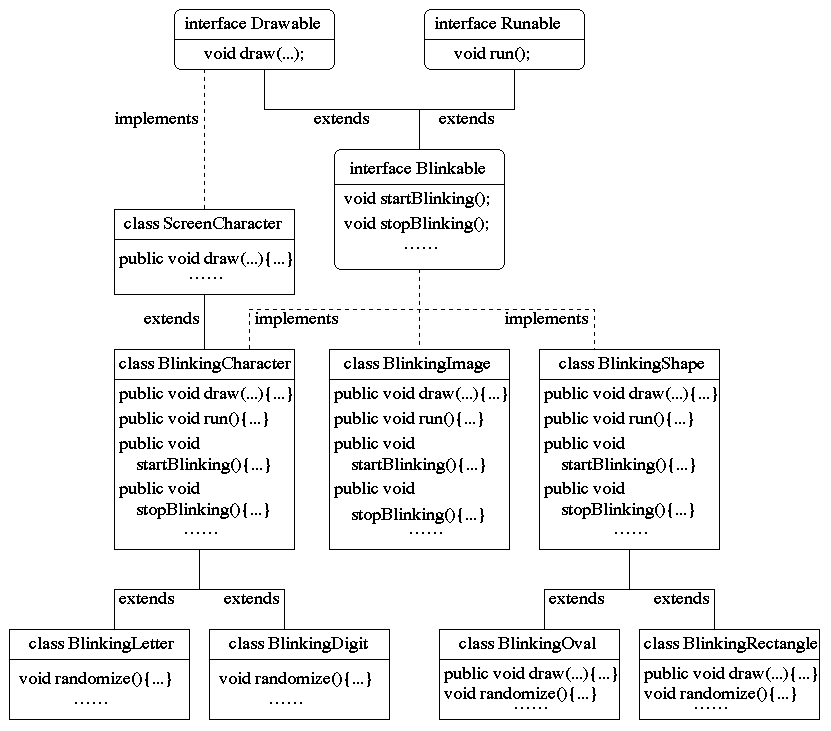
BlinkingObjects Example

Drawable and BlinkableDrawable and Blinkable
import java.awt.Graphics;
interface Drawable {
void draw (Graphics g);
}
interface Blinkable extends Runnable, Drawable {
float MAXRATE = 10; // maximum blinking rate is 10 flashes per second
float MINRATE = 0.1f; // minimum blinking rate is 1 flash per 10 seconds
void startBlinking();
void stopBlinking();
void setBlinkingRate(float r);
float getBlinkingRate();
}
import java.awt.*;
class ScreenCharacter implements Drawable {
...
public void draw(Graphics g) {
...
}
}
The definition of the class is the same as before.
import java.applet.Applet;
import java.awt.*;
class BlinkingCharacter extends ScreenCharacter implements Blinkable {
Applet applet;
float blinkingRate = MAXRATE;
int laptime = (int) (1/blinkingRate);
private Thread blinker = null;
private boolean isVisibleQ = true;
BlinkingCharacter(Applet applet) {
// constructor for default initialization
this("a", 12, 0, 0, applet);
}
BlinkingCharacter(String name, int fontsize, int x, int y, Applet applet) {
// constructor to initialize letter and position
super(name, fontsize, x, y);
this.applet = applet;
}
void randomize() {
int laptime = randomNumber(500,2000);
setBlinkingRate((float) 1/laptime);
super.randomize();
}
public void draw(Graphics g) {
if (isVisibleQ) {
super.draw(g);
}
}
public void run () {
while (blinker != null) {
applet.repaint();
...
isVisibleQ = !isVisibleQ;
}
}
public void startBlinking () {
...
}
public void stopBlinking () {
...
}
public float getBlinkingRate () {
return blinkingRate;
}
public void setBlinkingRate (float r) {
blinkingRate = Math.max(MINRATE, Math.min(r, MAXRATE));
}
}
import java.applet.Applet;
import java.awt.*;
class BlinkingLetter extends BlinkingCharacter {
String letterCase;
BlinkingLetter (Applet applet) {
this("a", 12, 0, 0, "lowercase", applet);
}
BlinkingLetter (String name, int fontSize, int x, int y,
String letterCase, Applet applet) {
super(name, fontSize, x, y, applet);
setCase(letterCase);
}
void toLowercase() {
letterCase = "lowercase";
name = name.toLowerCase();
}
void toUppercase() {
letterCase = "uppercase";
name = name.toUpperCase();
}
void randomize() {
// random name
int i = randomNumber(0,25);
name = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz".substring(i,i+1);
// random case
if (randomNumber(0,1) == 0) {
toLowercase();
}
else {
toUppercase();
}
// random other properties
super.randomize();
}
}
import java.applet.Applet;
import java.awt.*;
class BlinkingDigit extends BlinkingCharacter {
BlinkingDigit (Applet applet) {
this("1", 12, 0, 0, applet);
}
BlinkingDigit(String name, int fontsize, int x, int y,
Applet applet) {
super(name, fontsize, x, y, applet);
}
void randomize() {
// random digit
int i = randomNumber(0,9);
name = "0123456789".substring(i,i+1);
// random other properties
super.randomize();
}
}
import java.applet.Applet;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.*;
public class BlinkingObjectsApplet extends Applet {
Vector objects = new Vector();
...
public void init() {
add(new Button("new object"));
newObject(this);
}
public void start() {
Enumeration e = objects.elements();
Blinkable obj;
while (e.hasMoreElements()) { // step through all vector elements
obj = (Blinkable) e.nextElement();
obj.startBlinking();
}
}
public void stop() {
Enumeration e = objects.elements();
Blinkable obj;
while (e.hasMoreElements()) { // step through all vector elements
obj = (Blinkable) e.nextElement();
obj.stopBlinking();
}
}
public boolean action(Event e, Object arg) {
newObject(this);
repaint();
return(true);
}
public void paint(Graphics g) {
update(g);
}
public void update(Graphics g) {
...
Enumeration e = objects.elements();
Blinkable obj;
while (e.hasMoreElements()) { // step through all vector elements
obj = (Blinkable) e.nextElement();
obj.draw(offGraphics);
}
//Paint the image onto the screen.
g.drawImage(offImage, 0, 0, this);
}
void newObject(Applet applet) {
BlinkingCharacter c;
BlinkingShape s;
if (0 == (int) Math.round(Math.random())) {
// select character
if (0 == (int) Math.round(Math.random())) {
c = new BlinkingLetter(applet);
}
else {
c = new BlinkingDigit(applet);
}
c.randomize(); // choose random properties of character
c.startBlinking();
objects.addElement(c);
}
else {
// select shape
if (0 == (int) Math.round(Math.random())) {
s = new BlinkingOval(applet);
}
else {
s = new BlinkingRectangle(applet);
}
s.randomize(); // choose random properties of shape
s.startBlinking();
objects.addElement(s);
}
}
}
In the source code, in the methods start, stop, and
update, you can see that we step each time through the vector of
blinkable objects. Let us look more closely at the code for the
start method
Enumeration e = objects.elements();
Blinkable obj;
while (e.hasMoreElements()) { // step through all vector elements
obj = (Blinkable) e.nextElement();
obj.draw(offGraphics);
}
In the first line, all elements of the vector object are
placed in an Enumeration object. This is a container for
objects, and here we mean literally instances of the Object
class. We want to specify that the objects present in this container have the
property of being Blinkable. We declare the
Blinkable object obj so that whenever we select an
element in the container, we can cast its type to Blinkable,
assign it to the variable obj and we can send messages of the
Blinkable interface to this object without knowing whether it
is a blinking character, blinking oval shape, or a blinking rectangle.