TCP Throughput Tests
Description
There were also TCP throughput bulk data transfer tests executed
between Geneva and Chicago. To be able to compare the results with the
previously obtained
Netherlight results tests with two host pairs were executed, but there
were also tests with five host pairs performed. All tests were executed
bi-directional between Geneva and Chicago. For the two host pair tests streams
between w05gva-ge-0 <-> w05chi-ge-1 and
w06gva-ge-0 <-> w06chi-ge-1. The streams for the
five host pair test were formed correspondingly with the exception that the
hosts w04gva and w04chi were not participating in the tests
due to the unavailability of host w04chi.
In both setups the TCP throughput has been measured as a function of
the total # streams and the overall sum of the TCP window. The
Iperf tool has been used as
traffic generator because it can execute multiple streams light-weighted, using
the pthread system calls. For each single measurement a test time
of 60 s has been used. That is sufficient to deal with the combination of
slow startup and the long round-trip times of the link (about 100 ms).
Results
Using two host pairs the following results were
obtained:
displays the total TCP throughput value, summed over all streams, as a
function of the total TCP window size, again summed over all streams,
and the # streams for the direction Geneva ->
Chicago. In
the equivalent results for the reverse direction are shown. In
the average TCP throughput per stream is presented as a function of the
TCP window size per stream for the direction Geneva ->
Chicago. The results for each # streams are represented by a
separate plot trace.
shows these results for the reverse direction.
In the following figures the equivalent results are presented as listed in the
previous paragraph, but here with five host pairs.
shows again the total throughput values as function of the total window size and
# streams for the direction Geneva -> Chicago,
while
gives the results for the reverse direction.
also presents the average throughput values for the individual # streams as
function of the window size per stream for the direction
Geneva -> Chicago and
displays these results for the reverse direction.
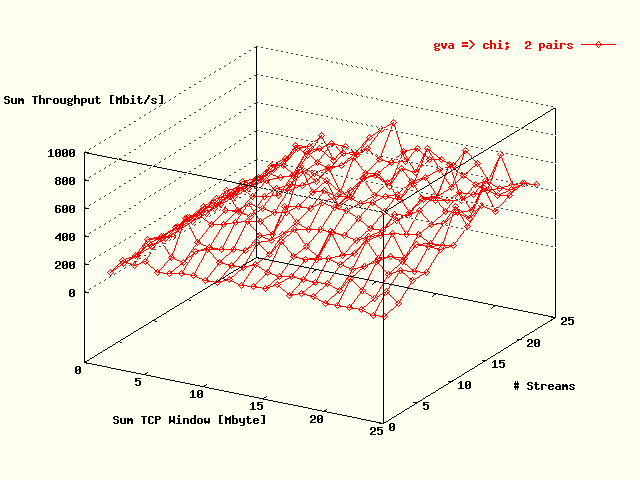
| . |
|
Total TCP throughput, summed over all streams,
as a function of the total TCP throughput, also
summed over all streams, and the # streams for the
direction Geneva -> Chicago.
Two host pairs were used in the tests. |
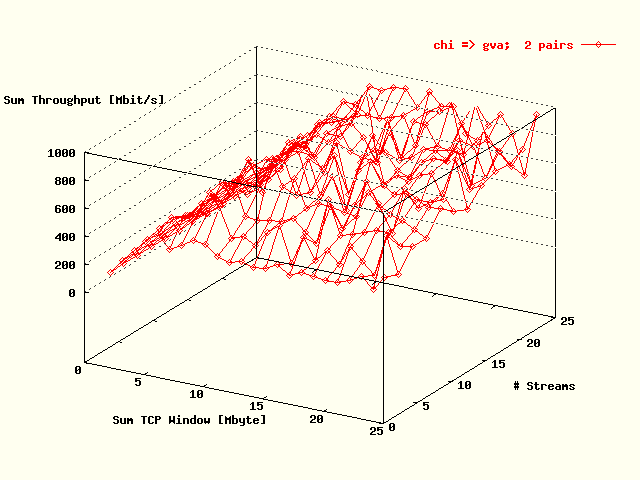
| . |
|
Total TCP throughput, summed over all streams,
as a function of the total TCP throughput, also
summed over all streams, and the # streams for the
direction Chicago -> Geneva.
Two host pairs were used in the tests. |
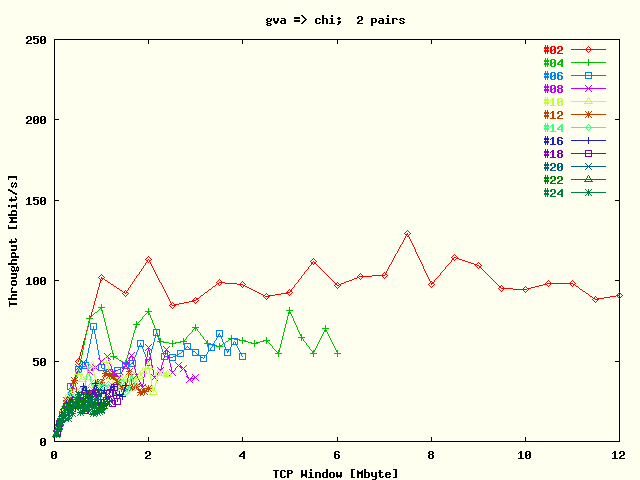
| . |
|
Average TCP throughput per stream as a function
of TCP window size for the direction
Geneva -> Chicago. The results
for each # streams are represented by a separate
plot trace. The tests were run with two host
pairs. |
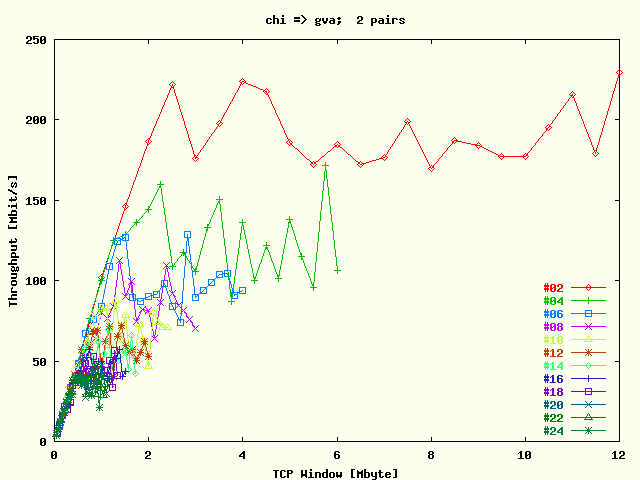
| . |
|
Average TCP throughput per stream as a function
of TCP window size for the direction
Chicago -> Geneva. The results
for each # streams are represented by a separate
plot trace. The tests were run with two host
pairs. |
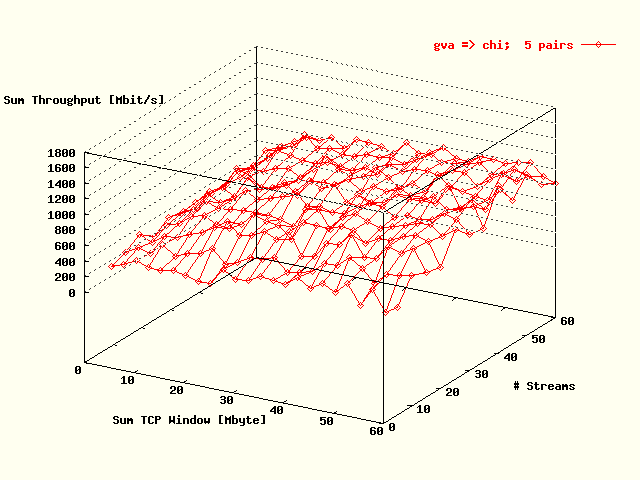
| . |
|
Total TCP throughput, summed over all streams,
as a function of the total TCP throughput, also
summed over all streams, and the # streams for the
direction Geneva -> Chicago.
Five host pairs were used in the tests. |
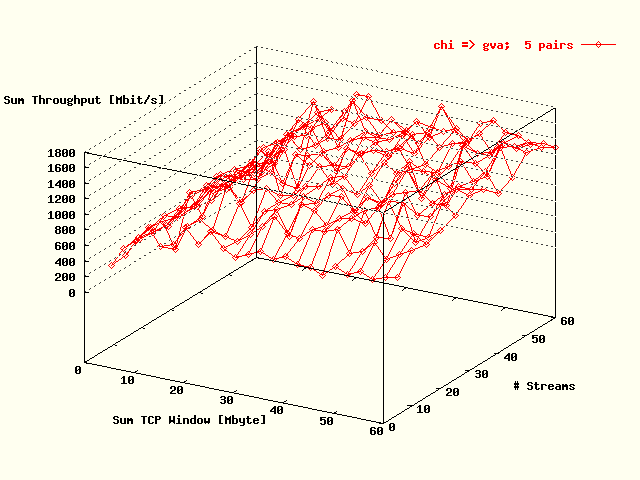
| . |
|
Total TCP throughput, summed over all streams,
as a function of the total TCP throughput, also
summed over all streams, and the # streams for the
direction Chicago -> Geneva.
Five host pairs were used in the tests. |
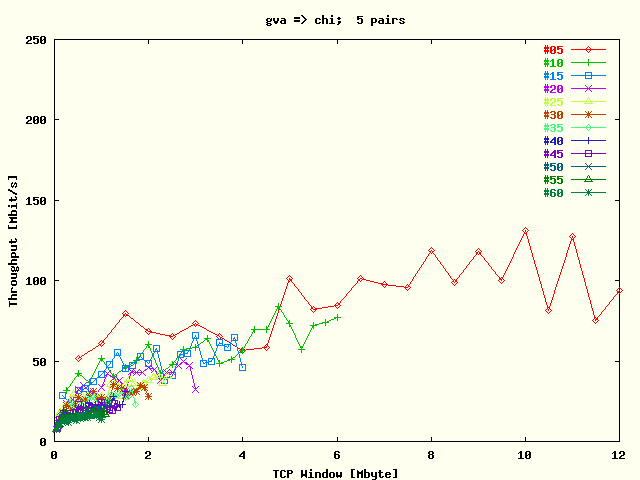
| . |
|
Average TCP throughput per stream as a function
of TCP window size for the direction
Geneva -> Chicago. The results
for each # streams are represented by a separate
plot trace. The tests were run with five host
pairs. |
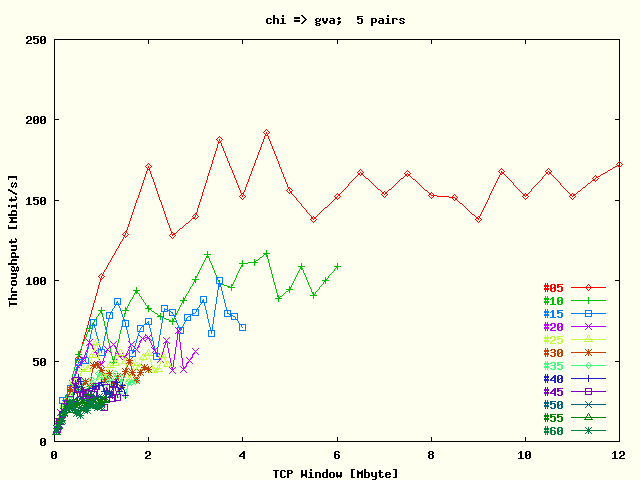
| . |
|
Average TCP throughput per stream as a function
of TCP window size for the direction
Chicago -> Geneva. The results
for each # streams are represented by a separate
plot trace. The tests were run with five host
pairs. |
Conclusions
From the
the following conclusions can be drawn:
-
The throughput in the direction Chicago -> Geneva
is considerable larger as in the direction Geneva ->
Chicago. The reason for that is not clear because the path in both
directions seems to be symmetric. Non-surprisingly also the average
throughput per stream in the direction Chicago ->
Geneva is much larger. Both statements hold for the tests with two
and five host pairs.
-
The maximum achieved throughput of about 1500 Mbit/s in the direction
Chicago -> Geneva is much less as could be
expected from a link with a provided bandwidth of 2.5 Gbit/s.
-
When the results from the DataTAG link for two host pairs are compared with
the corresponding
Netherlight results, the following can be concluded:
-
The 3D DataTAG figures are much more noisy than the corresponding
Netherlight results. This could be explained from the fact that in the
DataTAG circuit two routers are involved, while there was only one
router used in the Netherlight circuit.
-
The differences between a single and twelve streams per host pair in the
DataTAG network is less as in the Netherlight network. This is probably
also caused by the larger availability of routing power: there is more
network buffer capacity available to deal with the burstiness of the
TCP traffic send by the hosts. This is also clear from the
2D average throughput per stream plots. In the DataTAG network the
average throughput per stream is larger when the # streams are
smaller, while in the Netherlight network a sort of boundary seems to be
reached when the window size is increasing. In these Netherlight the
"#2" streams plot traces are even decreasing until the
boundary has been reached. In the DataTAG plots the average throughput
# streams plot traces are never lowering with increasing
TCP window size.
UDP Bulk Transfer Tests
Description
Also UDP bulk data transfer tests were executed between Geneva
and Chicago in both directions. The same two host pairs as for the
TCP tests were used. Also three host pair
tests were executed, where streams between hosts w02gva-ge-0 and
w02chi-ge-1 had been add to the streams used in the two host pair
tests. Also here the Iperf
application had been used to generate the UDP traffic.
The shaped UDP bandwidth send per stream had been varied until and
including 1000 Mbit/s with a step size of 12 Mbit/s. At each source
host one to four streams had been started to the corresponding destination host.
Again the pthread system library had been used to start the
multiple streams. In these tests the # packets lost were measured as a
function of the total shaped UDP bandwidth and the # streams for
both directions Geneva <-> Chicago.
Results
From these tests the following results were obtained:
-
At none of the tests with two host pairs significant packets loss had been
detected. When three host pairs were used, steep racing packets lost above
receiver bandwidths of 2300 Mbit/s using one stream per host pair.
-
For single streams per host pair the maximum total bandwidth without packets
lost was in both directions about 1910 Mbit/s with two host pairs and
about 2330 Mbit/s for three host pairs.
-
For multiple streams per host out-of-order packets had been detected and the
reported bandwidths for servers and clients seemed not to be completely
reliable for total bandwidths larger than 700 - 800 Mbit/s. Local
tests at single and dual processor hosts from our cluster at
SARA with
Iperf streams, using the
pthread library or alternatively multiple processes to start
multiple streams showed that:
-
The out-of-order packets and the observed errors in the reported
bandwidths were also found for the local tests with dual processor hosts
when multiple streams per host in combination with the
pthread library had been used. This implies that the
out-of-order packets, mentioned before, were probably not induced by the
network.
-
For single processor hosts and with usage of the
pthread
library, no out-of-order packets and bandwidth reporting errors had been
found. Until know that were also our experiences with the
Iperf tool.
-
With dual processor hosts and without usage of the
pthread
library no out-of-order packets and bandwidth reporting errors had been
found. The reason probably is that each stream process is completely
handled by one processor, but this might be no guarantee that these
errors will never occur.
Also these results will be compared with the corresponding
Netherlight results.
Conclusions
From the UDP bulk data transfer tests executed at the DataTAG link and
the Netherlight Lambda the following can be concluded:
-
Packets loss is only found for single stream tests using three host pairs
with a bandwidth of about 2330 Mbit/s. These values are in reasonable
agreement with the line speed of 2.5 Gbit/s.
-
The out-of-order packets and unreliability in bandwidth reports, only found
in multiple stream tests when the
pthread library had been
used, where host effects.
-
The achieved bandwidth at the DataTAG network is larger than at the
Netherlight network.







