Level(3) Lambda UDPmon Large Monitor Results (4 * STS 12C)
Description
In this document UDP experiments are described that were performed with a
modified version of the UDPmon
package written by R.E. Hughes-Jones in the sense that from
5000 packets the sequence number and the arrival time in microsec. are
specified. The experiments were executed at the
Level(3) Lambda before acceptance by
SURFnet. All tests were performed after
the hosts upgrade of the SARA cluster to
515 Mbyte memory and Linux V.2.4.16-web100.
An overview and description of the tests at the preceding
Teleglobe Lambda can be found in this
document. During those tests the Lambda, the hosts
hardware and OS were in various upgrade states.
Results
Topology
For the tests, described below, the topology has been used that is given in
.
SARA
+----------+ EVL
| gwgsara2 |-\
+----------+ \ +---+ +----------+
\ +---+ STS 12C +---+ | 6 | /-| prusin |
+----------+ \--| |- ......... -| |-----| 5 |--/ +----------+
| gwgsara4 |--\ | 1 | | 1 | | 0 |
+----------+ \---| 5 |- ......... -| 5 |-----| 9 |--\ +----------+
| 4 | | 4 | +---+ \-| reynolds |
+----------+ /---| 5 |- ......... -| 5 |--\ +----------+
| gwgsara3 |--/ | 4 | | 4 | |
+----------+ /--| |- ......... -| |--/ hard
/ +---+ +---+ loop-back
+----------+ /
| gwgsara5 |-/
+----------+
|
| . |
|
Topology of the used connection scheme. All hosts are
directly connected with the ONS15454. Hosts
gwgsara2 and gwgsara4 are connected
with the LSD6509, while the hosts gwgsara3 and
gwgsara5 are internally connected via a hard
loop-back at the ONS15454 in Chicago. Four STS 12C
channels are used between both
ONS15454's. |
Time-sequence plots
In these tests 5000 packets were send with zero wait time between two
successive packets. The packets were send with packet sizes of 500, 1000, 1200
and 1460 byte. From these data time-sequence plots have been created, where
the time difference with the first packet has been plotted as a function of the
packet sequence number. When a packet got lost the time difference will be set
to zero.
In
the time-sequence data are shown for the stream gwgsara2 =>
prusin and in the
for the reverse direction. In the
these data are given for the stream gwgsara2 =>
gwgsara4 (via the LSD6509, Chicago) and in the
for the reverse direction. The
are presenting these data for the stream gwgsara3 =>
gwgsara5 (via the hard loop-back in the ONS15454, Chicago) and in the
the time-sequence data for the reverse direction are presented.
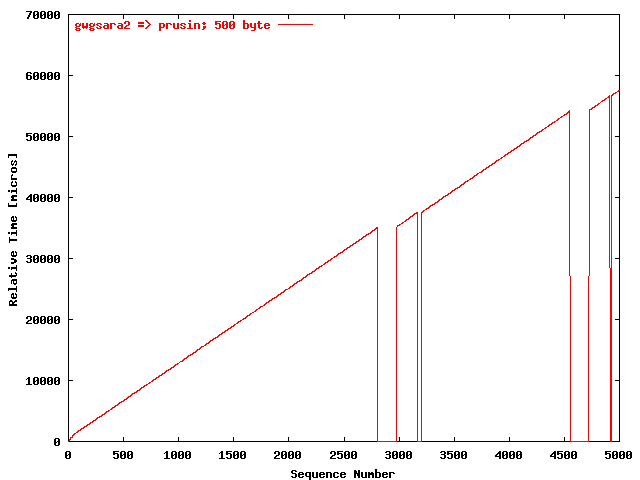
| .I. |
|
The relative receiving time as a function of the packet
sequence number for the UDP stream
gwgsara2 => prusin. The packet
size was 500 byte. |
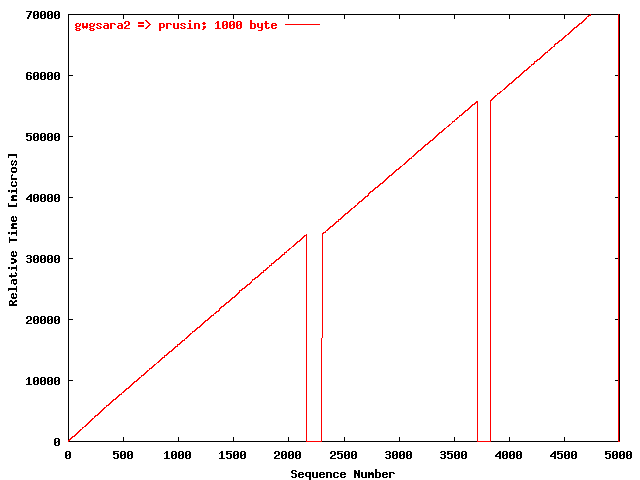
| .II. |
|
The relative receiving time as a function of the packet
sequence number for the UDP stream
gwgsara2 => prusin. The packet
size was 1000 byte. |
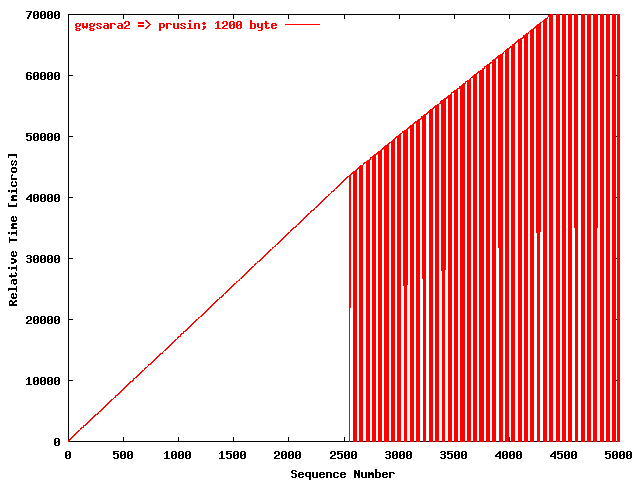
| .III. |
|
The relative receiving time as a function of the packet
sequence number for the UDP stream
gwgsara2 => prusin. The packet
size was 1200 byte. |
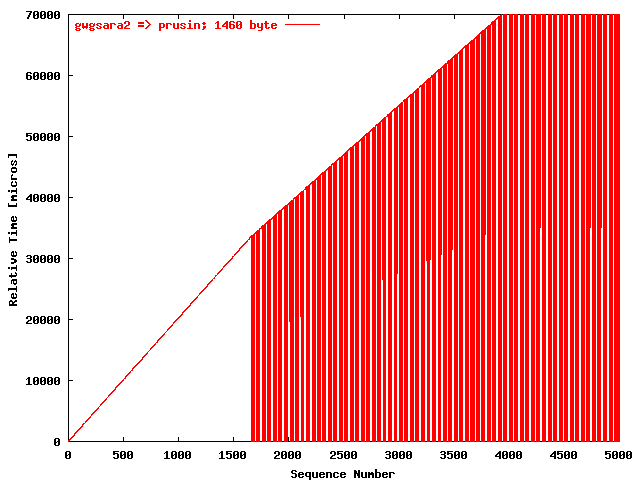
| .IV. |
|
The relative receiving time as a function of the packet
sequence number for the UDP stream
gwgsara2 => prusin. The packet
size was 1460 byte. |
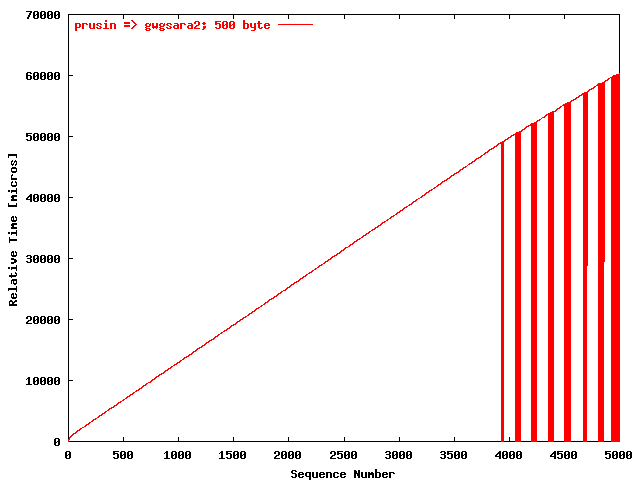
| .I. |
|
The relative receiving time as a function of the packet
sequence number for the UDP stream
prusin => gwgsara2. The packet
size was 500 byte. |
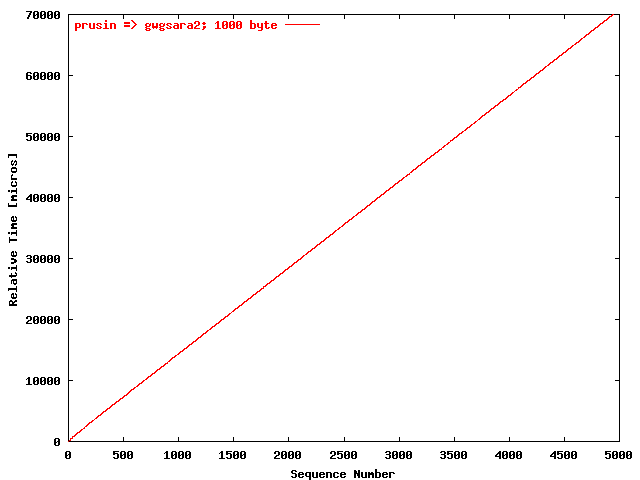
| .II. |
|
The relative receiving time as a function of the packet
sequence number for the UDP stream
prusin => gwgsara2. The packet
size was 1000 byte. |
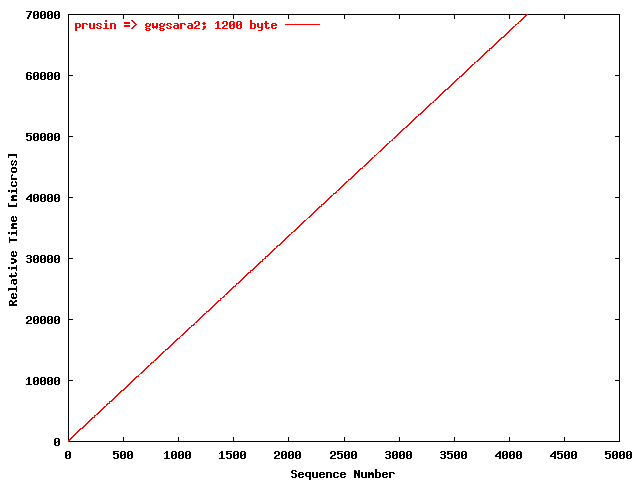
| .III. |
|
The relative receiving time as a function of the packet
sequence number for the UDP stream
prusin => gwgsara2. The packet
size was 1200 byte. |
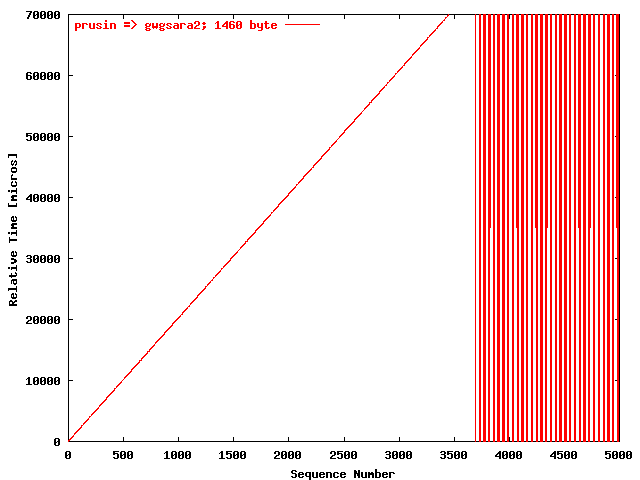
| .IV. |
|
The relative receiving time as a function of the packet
sequence number for the UDP stream
prusin => gwgsara2. The packet
size was 1460 byte. |
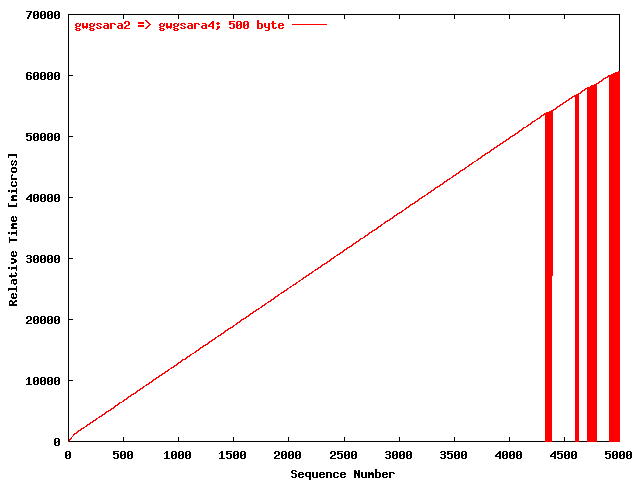
| .I. |
|
The relative receiving time as a function of the packet
sequence number for the UDP stream
gwgsara2 => gwgsara4 (via the
LSD6509, Chicago). The packet size was
500 byte. |
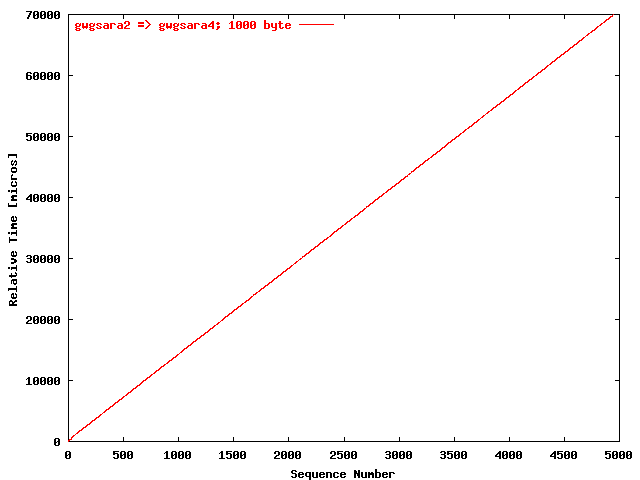
| .II. |
|
The relative receiving time as a function of the packet
sequence number for the UDP stream
gwgsara2 => gwgsara4 (via the
LSD6509, Chicago). The packet size was
1000 byte. |
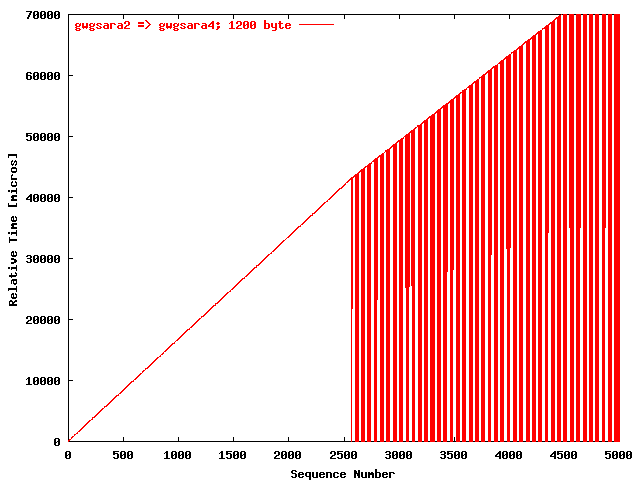
| .III. |
|
The relative receiving time as a function of the packet
sequence number for the UDP stream
gwgsara2 => gwgsara4 (via the
LSD6509, Chicago). The packet size was
1200 byte. |
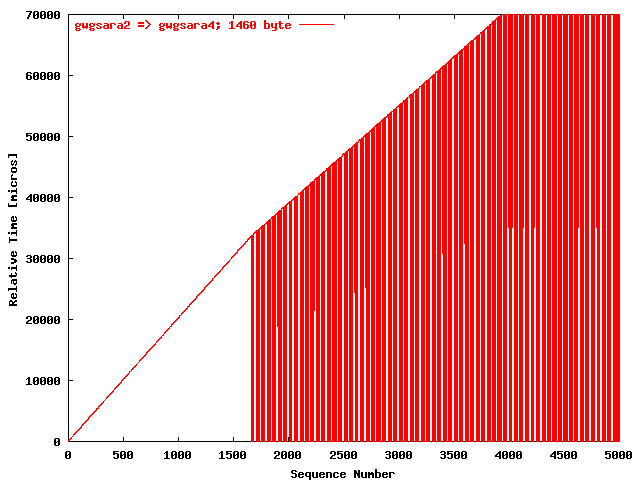
| .IV. |
|
The relative receiving time as a function of the packet
sequence number for the UDP stream
gwgsara2 => gwgsara4 (via the
LSD6509, Chicago). The packet size was
1460 byte. |
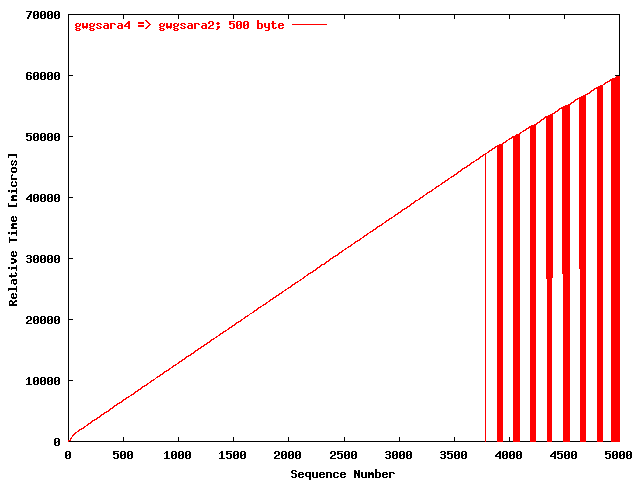
| .I. |
|
The relative receiving time as a function of the packet
sequence number for the UDP stream
gwgsara4 => gwgsara2 (via the
LSD6509, Chicago). The packet size was
500 byte. |
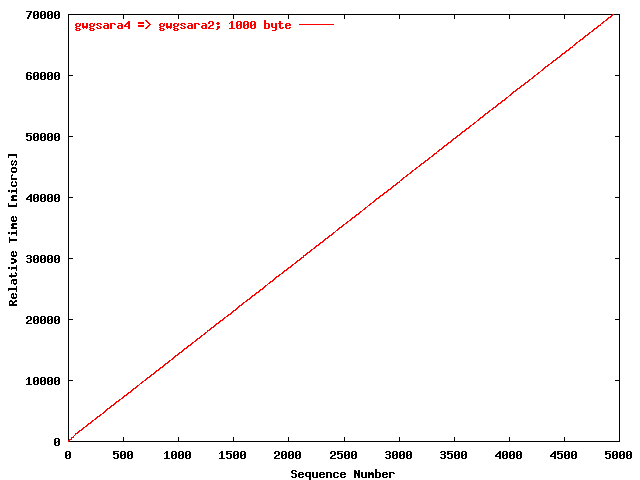
| .II. |
|
The relative receiving time as a function of the packet
sequence number for the UDP stream
gwgsara4 => gwgsara2 (via the
LSD6509, Chicago). The packet size was
1000 byte. |
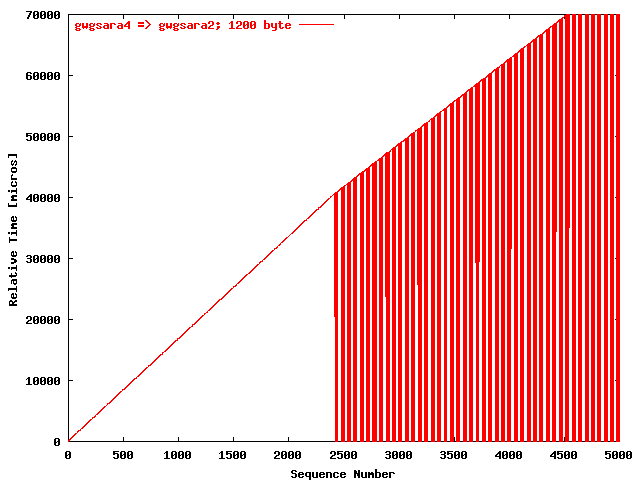
| .III. |
|
The relative receiving time as a function of the packet
sequence number for the UDP stream
gwgsara4 => gwgsara2 (via the
LSD6509, Chicago). The packet size was
1200 byte. |
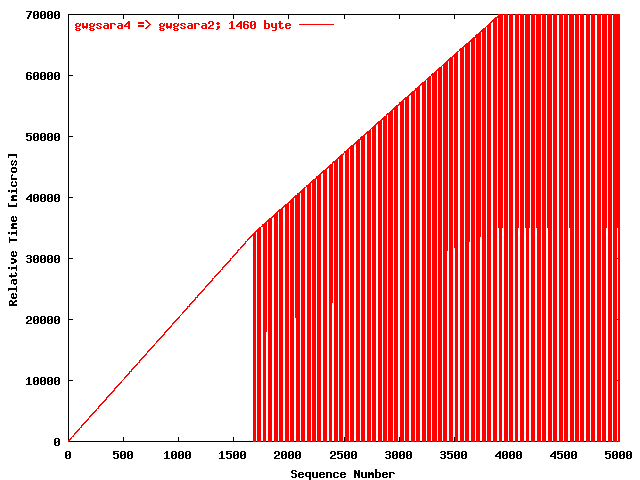
| .IV. |
|
The relative receiving time as a function of the packet
sequence number for the UDP stream
gwgsara4 => gwgsara2 (via the
LSD6509, Chicago). The packet size was
1460 byte. |
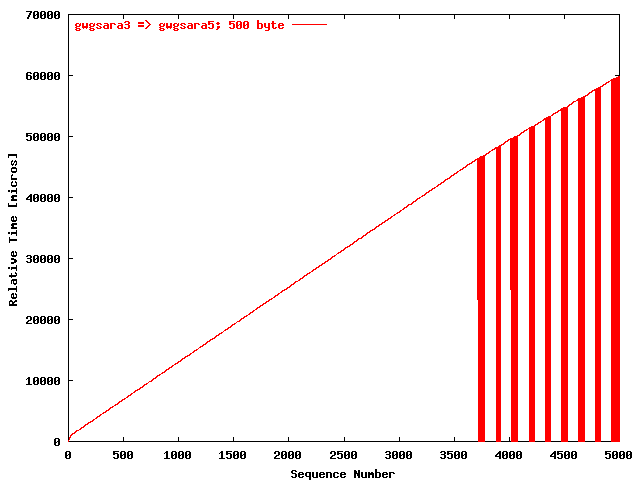
| .I. |
|
The relative receiving time as a function of the packet
sequence number for the UDP stream
gwgsara3 => gwgsara5 (via the
hard loop-back in the ONS15454, Chicago). The packet
size was 500 byte. |
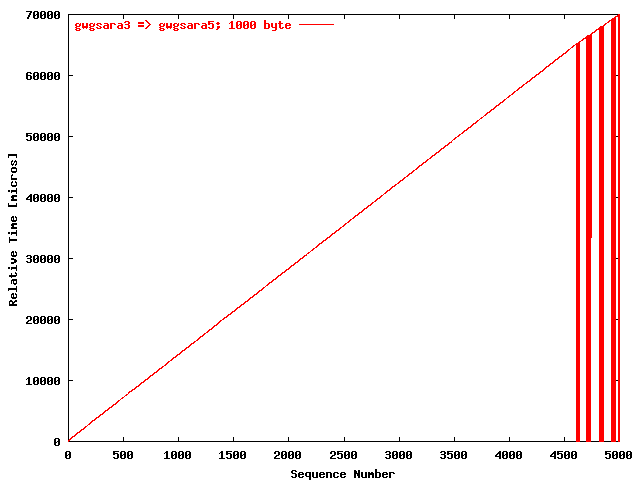
| .II. |
|
The relative receiving time as a function of the packet
sequence number for the UDP stream
gwgsara3 => gwgsara5 (via the
hard loop-back in the ONS15454, Chicago). The packet
size was 1000 byte. |
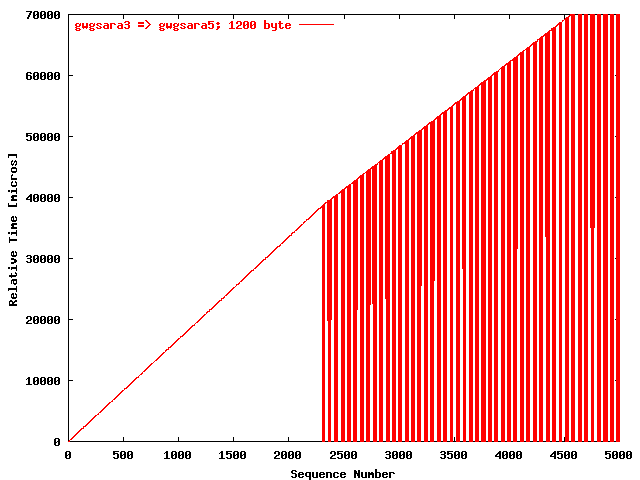
| .III. |
|
The relative receiving time as a function of the packet
sequence number for the UDP stream
gwgsara3 => gwgsara5 (via the
hard loop-back in the ONS15454, Chicago). The packet
size was 1200 byte. |
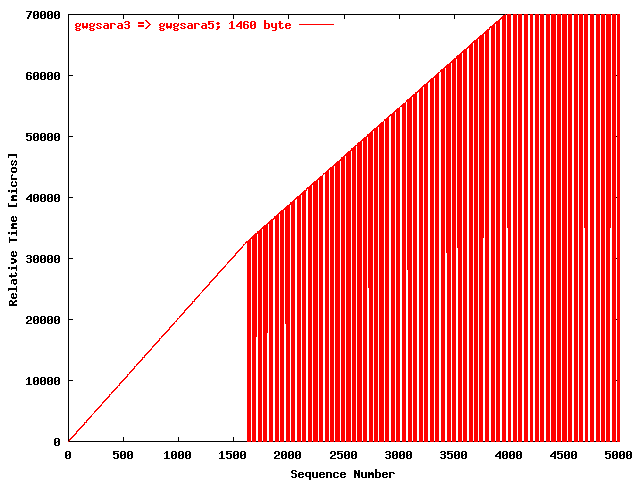
| .IV. |
|
The relative receiving time as a function of the packet
sequence number for the UDP stream
gwgsara3 => gwgsara5 (via the
hard loop-back in the ONS15454, Chicago). The packet
size was 1460 byte. |
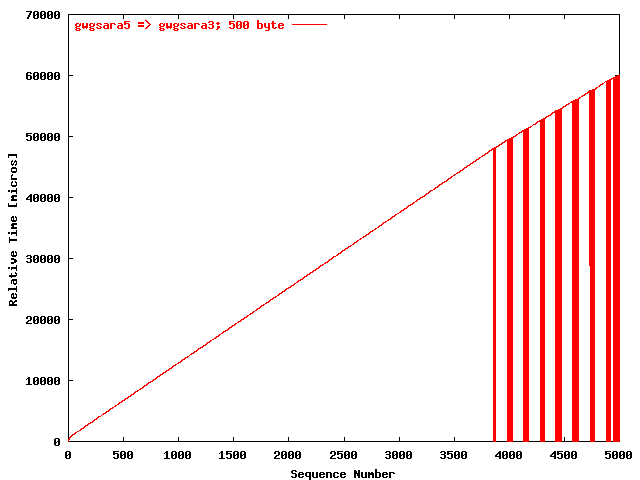
| .I. |
|
The relative receiving time as a function of the packet
sequence number for the UDP stream
gwgsara5 => gwgsara3 (via the
hard loop-back in the ONS15454, Chicago). The packet
size was 500 byte. |
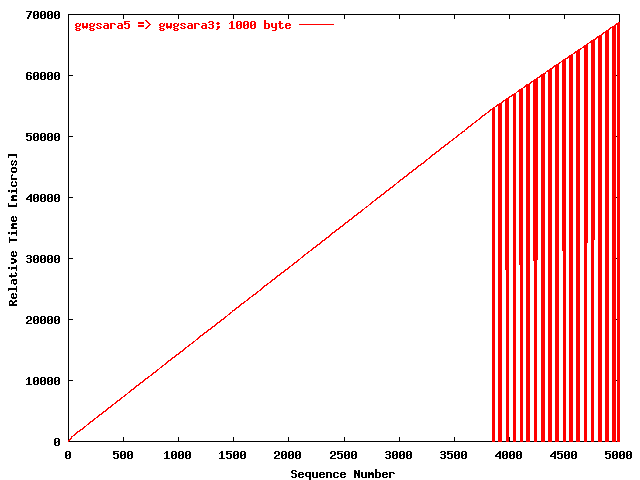
| .II. |
|
The relative receiving time as a function of the packet
sequence number for the UDP stream
gwgsara5 => gwgsara3 (via the
hard loop-back in the ONS15454, Chicago). The packet
size was 1000 byte. |
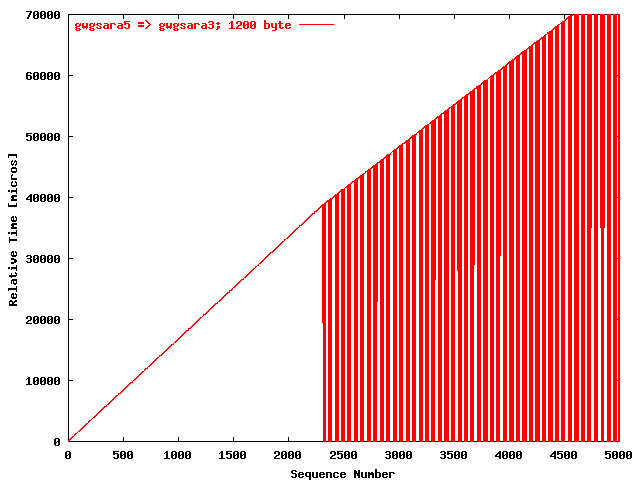
| .III. |
|
The relative receiving time as a function of the packet
sequence number for the UDP stream
gwgsara5 => gwgsara3 (via the
hard loop-back in the ONS15454, Chicago). The packet
size was 1200 byte. |
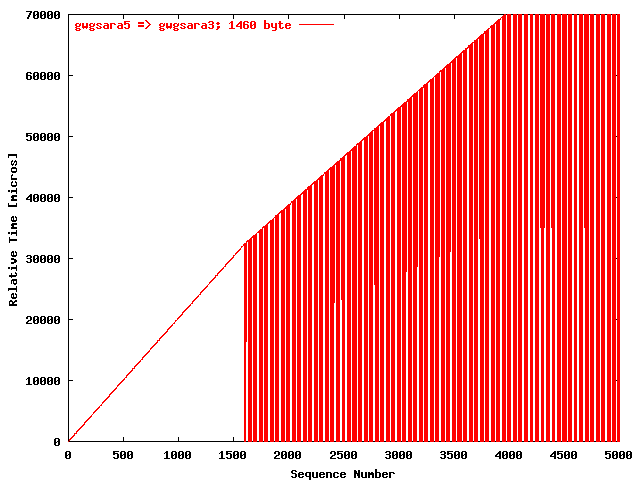
| .IV. |
|
The relative receiving time as a function of the packet
sequence number for the UDP stream
gwgsara5 => gwgsara3 (via the
hard loop-back in the ONS15454, Chicago). The packet
size was 1460 byte. |
Bandwidth and memory network bottleneck estimation table
The time-sequence data can also be used to estimate
a.o. the parameters discussed in the following subsections.
Bandwidth
From the # received packets and the packet size in bytes size, the
bandwidth can be calculated
with
with:
|
B
|
|
: |
|
The bandwidth.
|
|
Nrecv
|
|
: |
|
The # received packets.
|
|
Spacket
|
|
: |
|
The packet size in byte.
|
|
Trecv
|
|
: |
|
The time required to receive the packets.
|
is used to calculate the bandwidth from the areas without and with packets loss
in the time-sequence plots.
Memory estimation of the network bottleneck
With the used topology with 4 * STS 12C
channels, the provided bandwidth per channel is limited to 622 Mbit/s. Due
to that limitation packet loss will occur which makes it possible to make an
estimation of the involved network memory bottleneck by following the
argumentation of the
"Level(3) Lambda UDPmon Large with STS Tuning" document.
shows as a function of the used streams and packet sizes the following
parameters denoted with the corresponding table headers:
-
Stream
-
The stream for which the parameters are specified.
-
Spacket
-
The packet size in byte.
-
Bno-loss
-
The bandwidth in the area without packet loss, calculated
with
in Mbit/s.
-
Bloss
-
The bandwidth in the area with packet loss, calculated
with
in Mbit/s. When there is no packet loss the corresponding table cell is
empty.
-
Ilast
-
The sequence number from the last packet in the area without loss.
-
Nloss
-
The number packets lost.
-
Mmem
-
The memory of the network bottleneck. Also here the table cell is empty when
no memory value could be estimated because there was no lost.
|
Stream
|
Spacket
[byte]
|
Bno-loss
[Mbit/s]
|
Bloss
[Mbit/s]
|
Ilast
|
Nloss
|
Mmem
[Kbyte]
|
|
gwgsara2 => prusin
|
500 |
320 |
319 |
2802 |
399 |
260 |
| 1000 |
510 |
517 |
2160 |
265 |
202 |
| 1200 |
562 |
563 |
2553 |
394 |
492 |
| 1460 |
576 |
577 |
1661 |
705 |
508 |
|
prusin => gwgsara2
|
500 |
320 |
328 |
3925 |
152 |
284 |
| 1000 |
565 |
|
4999 |
0 |
|
| 1200 |
571 |
|
4999 |
0 |
|
| 1460 |
576 |
578 |
3692 |
121 |
495 |
|
gwgsara2 => gwgsara4
|
500 |
322 |
329 |
4328 |
103 |
340 |
| 1000 |
566 |
|
4999 |
0 |
|
| 1200 |
571 |
573 |
2568 |
393 |
496 |
| 1460 |
575 |
577 |
1658 |
705 |
507 |
|
gwgsara4 => gwgsara2
|
500 |
321 |
327 |
3785 |
174 |
278 |
| 1000 |
565 |
|
4999 |
0 |
|
| 1200 |
570 |
572 |
2418 |
445 |
498 |
| 1460 |
575 |
577 |
1682 |
689 |
506 |
|
gwgsara3 => gwgsara5
|
500 |
320 |
328 |
3715 |
189 |
280 |
| 1000 |
566 |
566 |
4610 |
49 |
581 |
| 1200 |
572 |
573 |
2308 |
468 |
480 |
| 1460 |
577 |
577 |
1622 |
725 |
505 |
|
gwgsara5 => gwgsara3
|
500 |
321 |
329 |
3853 |
162 |
279 |
| 1000 |
564 |
569 |
3846 |
151 |
504 |
| 1200 |
571 |
573 |
2309 |
484 |
497 |
| 1460 |
576 |
577 |
1597 |
728 |
495 |
| . |
|
The bandwidth in the areas with and without packets
loss, the highest sequence number without loss, the
# packets lost, and the memory of the network
bottleneck as a function of the stream and the packet
size. |
Conclusions
From the time-sequence plots and
bandwidth and memory network bottleneck estimation table the following
conclusions can be drawn:
-
The packets loss in the direction gwgsara2 =>
prusin for packet sizes less equal 1000 byte are probably
caused by the more limited CPU power of the latter host.
-
In all other cases the packets loss are probably caused in the network.
-
As in the
"Level(3) Lambda UDPmon Large with STS Tuning" document,
realistic values for the memory network bottleneck are found for the packet
sizes larger equal 1260 byte. In that area the achieved bandwidth is
limited by the provisioned bandwidth of 622 Mbit/s.
^ All Level(3) Lambda UDPmon Large Results |
Teleglobe Lambda UDPmon Large Results























