

Next: Presentation results and data
Up: Description and Requirements
Previous: Description and Requirements
In this section a description of the RTPL package ( Remote
Throughput, Ping and Load) is given in more detail. As already explained
in the introduction, this package does periodically net performance
measurements between a set of hosts. The measurements are performed by
a, so called, control host. This workstation starts the net performance
measurements at each of the participating workstations with a, so
called,
remote shell command1.
Also the results of the measurements are send back via the remote shell
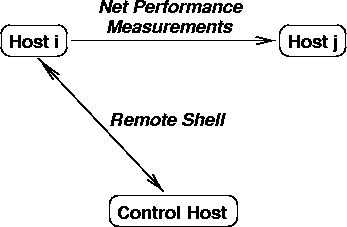
command. This process is schemed in figure 1.
Figure:
The control host starts the measurements at all
hosts i by means of remote shells. The host i performs the measurements to the hosts j The results
are send back by host i to the control
host.
 |
At each host i of the set hosts, described above, the following net
performance measurements are executed:
-
- Throughput.
-
Formal definition from RFC 1224 [2]: ``The maximum
rate at which none of the offered frames are dropped by the
device''. It is a way to quantify the traffic flow which can be
handled by a network connection. Default it is measured for the
connections from the current host i to all other hosts, but it
is also possible to skip connections. The throughput is measured
with the public domain command netperf.
- Roundtrip or Ping.
-
This Internet application is described in
RFC 2151 [3] by the paragraph quoted below:
Ping, reportedly an acronym for the Packet Internetwork
Groper, is one of the most widely available tools bundled
with TCP/IP software packages. Ping uses a series of
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) [4] Echo
messages to determine if a remote host is active or
inactive, and to determine the round-trip delay in
communicating with it.
The roundtrip time quantifies the response offered by a network
connection. It will be measured, before the throughput, across
the same connections as the throughput. The roundtrip time is
measured with the system command ping.
- Load.
-
This is expressed here as # fully active processes at a host.
It is no network quantity, but it may help to explain unexpected
performance decreases. The load is measured at the current
host i, using the system command uptime.
The sampling of the results at the control host and the measurements at
all hosts, participating in the tests, are performed by scripts in the
scripting language Perl. Perl is a powerful scripting language
which is available for many platforms, including Unix, Windows NT/9Xand MacOS.
The Perl script at the control host collects the results of the
measurements for each host i and stores the results in ZIP compressed
data files. The ZIP compression is used to reduce disk space and
download time. See subsection 2.2 for a
description of the data files.
The tests are periodically started with the so called
crontab2
command. A sample crontab input file, which is specific for a
hosts set, will be generated at the installation of that set. When the
previous test is not ended when a new one is started by crontab,
the new test terminates. However, to prevent deadlocks, after some
terminations the new version kills the old one and continues. Timeouts
are used in the test scripts to prevent deadlocks.


Next: Presentation results and data
Up: Description and Requirements
Previous: Description and Requirements
Hans Blom
2000-02-22

